Bearings are the pillars that support the moving or rotating components of industrial machines. One instance of bearing failure can mean machine shutdown and hours of production loss. Thus, one of the critical areas of maintaining machines and equipment is bearing maintenance. Bearing maintenance involves monitoring and preventing unplanned bearing failure. An effective bearing maintenance plan begins and ends with proper lubrication. In this post, you will learn everything you need to know about proper bearing lubrication: its purpose, essential steps, and critical considerations.
Purpose of Bearing Lubrication
Bearings, both the rolling and sliding types, carry the load of moving machine parts while they are in contact with the surfaces of said parts. Therefore, bearings are constantly exposed to friction. Friction causes bearings to wear faster, producing heat and contaminants that damage machine parts.
Lubricants reduce friction and wear by creating a film between the surfaces of bearings and the machine parts they are in contact with. In addition, lubricants also help dissipate the heat produced by friction, create a seal that keeps contaminants out, inhibit corrosion, and keep rolling parts together during assembly.
But bearing lubrication is more than simply applying lubricants to bearing parts. Proper bearing lubrication strategies must be implemented to effectively control friction and extend the life of bearings. The following sections will discuss the critical elements of proper lubrication techniques.
Bearing Lubricant Selection
Proper bearing lubrication starts with selecting the ideal type of lubricant. The wrong lubricant, even when applied properly, can do more harm than good. The type of lubricant to use depends on the type of bearing, operating load and speed, process conditions, accessibility of lubrication, and other considerations. The following are the available types of lubricants with specific applications:
Grease Lubricants
Grease is the most commonly used type for bearing lubrication because it adheres better to bearings, has high corrosion protection, and provides longer surface protection. Under grease types, you can choose soap or non-soap-based grease. Depending on the water or heat resistance requirements of your bearings, you can further select what kind of soap base (lithium, calcium, or sodium) to use.
Oil Lubricants
Oil-type lubricants have low viscosity or are thinner than grease. Oils need more re-application than grease lubricants. Oils are more suited for bearings used in high-speed and high-temperature applications. These types are also ideal for machines that have limited accessibility or do not allow disassembly and require an oil-lubricating delivery system to lubricate.
Solid Lubricants
Solid lubricants are relatively new technologies and may be useful if grease and oil lubricants are not effective. Machine manufacturers may recommend special types of lubricants, including solid types, for their machines. Solid lubricants often come with high price tags but can deal with extreme temperature and pressure or special environments such as in a vacuum or with the presence of radiation, etc.
Proper Bearing Lubrication Steps
In addition to selecting the right lubricant, following the correct steps of lubrication is also critical to proper bearing lubrication. Below are the steps to properly apply or re-apply bearing lubricants:
- Prepare the applicator or grease gun, making sure that you have the right lubricant and enough amount for application. If using oil delivery systems, check whether the current level is within the recommended levels of your system.
- Prepare the machine and parts. Depending on lubrication recommendations, your machine may need to be running, running on standby, shut down, or disassembled. Also, you may need to cool down or heat some parts to be at the right temperature or pressure before application.
- Clean surfaces and surrounding areas. Cleaning removes contaminants such as water, dust, metal debris, etc. that may enter the bearing cavity and cause damage.
- Apply lubricant until the recommended levels are reached. Allow the excess oil or grease to be released by opening the drain fitting or removing the drain plug.
- Inspect and make sure that the excess grease or oil has been removed. Re-install the drain plugs and clean the remaining grease or oil from all surfaces.
- Reassemble the machine and restart it. Monitor the machine for any sign of malfunction, such as irregular noise or vibrations.
- If such signs are present, conduct the necessary inspection and troubleshooting. Otherwise, follow a regular monitoring schedule to keep an eye on signs of bearing malfunction.
Bearing Lubrication Frequency
The next thing to consider ensuring proper bearing lubrication is when and how frequently you should apply lubricants. The best way is to start with the recommendations of the machine or equipment manufacturer. These recommendations are based on their machine quality test, so make sure to check whether their testing conditions align with your operational conditions.
Furthermore, machine operators can also base their lubrication recommendations on a formula such as this:
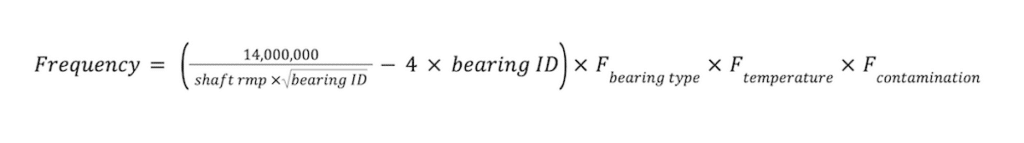
Where:
- Frequency = hours between lubrication
- Shaft rpm = shaft speed in revolutions per minute
- Bearing ID = bearing internal diameter in millimeters
- Fbearing type = factor for bearing type (1.0 for spherical thrust bearing, 5.0 for cylindrical, 10.0 for ball bearing)
- Ftemperature = factor for temperature (1.0 for under 160℉/71℃, divide by 2 for every 20℉/7℃ above 160℉/71℃)
- Fcontamination = factor for contamination (0.1 to 1.0 depending on the level of contamination)
On top of this formula, another way to identify the frequency of your lubrication schedule is by data analysis. The data you must consider include history of failure, past maintenance findings, vibration analysis results, and bearing test results. Consider also the unique conditions of the machines and the operator and technician’s knowledge.
Lubrication Management with Redlist
Proper bearing lubrication adds years to the service life of a machine or equipment. On the other hand, improper lubrication is the major cause of bearing issues and resulting machine failures. Thus, it becomes more important to implement a lubrication management program to ensure that lubricating bearings and other parts are done properly: with the right type and quantity, to the right point, and at the right time. Redlist’s Lubrication Management Software makes your lubrication program more accurate, efficient, and cost-effective.
Our digitized file storage makes it easy to access machine information such as lubrication instructions and recommendations. The user-friendly and mobile access-enabled platform also makes lubrication charting and scheduling easy and allows technicians to complete real-time and accurate reporting. Most importantly, Redlist keeps records of lubrication history, bearing issues, failures, and similar details.
These details help you analyze and evaluate your current lubrication program and make the necessary improvements. To learn more about how Redlist can boost your lubrication management program, schedule a free demo with a member of our team today!


